I built a low-cost, high-efficiency home theater computer with the new AM1 platform, which you can read about here. Energy efficient HTPC media center running Ubuntu. Now, we're giving it away. Read more . APU technology takes center stage within the AM1 platform, providing both a CPU and GPU in a single package. AM1 components require less space and need less overhead than conventional Intel and AMD processors. Lower wattage requirements open the door to picoPSU technology, which enables efficient conversion of 96 percent of power from the wall to your computer. Additionally, the platform performs well as a desktop, HTPC, or even a light Steam platform, at console resolutions.
However, DIYers should be aware of the ins and outs of the AM1 platform, particularly its integrated graphics (known as APUs). The heart and soul of a modern media center is its ability to deliver digital content to televisions. The AM1 platform design pushes more components into the APU, allowing manufacturers to get significant discounts on motherboards. AM1 boards are priced as low as $29.99. The system also offers lower power consumption than most budgets. The average build will require around 30 watts throughout normal operation. Its low costs, moderate performance, and energy efficiency make it an ideal platform for word processing, media center systems, and more.
This article covers the various components, with tips, for creating an AM1-based media center or office productivity desk. I also show the AM1 platform with three sample builds.

The AM1 platform specializes in a small but efficient number of roles. Please be aware of the following build restrictions:small form factors, limited SATA ports, and limited driver availability.
AM1 motherboards come in only two sizes:mini-ITX (mITX) and microATX (mATX). As far as I can tell, the only difference between a microATX and a mini-ITX card is the number of PCIe slots available. mITX cards have a single PCIe 2.0 x16 slot (quarter speed), while mATX cards offer at least one PCIe and one PCIe 2.0 x16 slot (quarter speed). A quarter-speed PCIe 2.0 port is electrically wired for the x16 form factor, but operates at quarter speed. For example:
mITX single port PCIe 2.0 x16 (quarter speed):
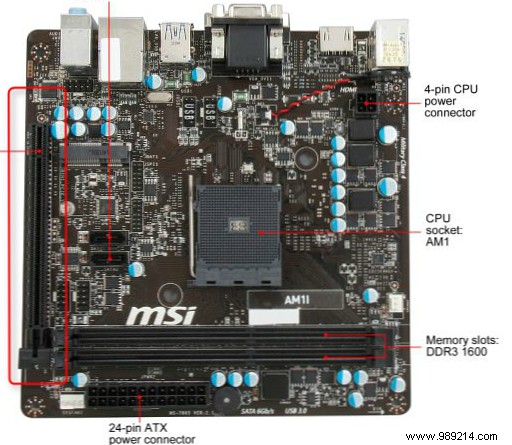
mATX PCIe + PCIe 2.0 x16 (quarter speed):
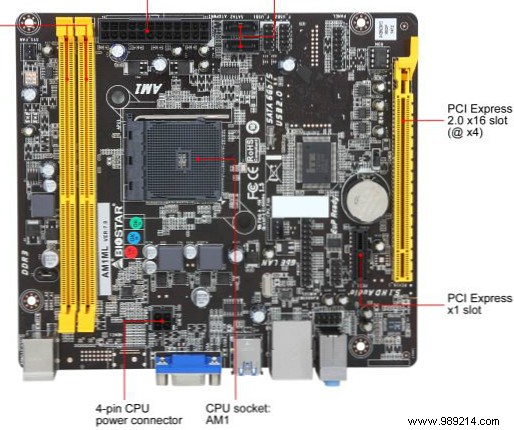
By design, vanilla AM1 plugged-in motherboards feature only two SATA III ports. This limits the roles that the AM1 platform can fulfill; for example, most media centers only need one or two SATA ports. A file server, on the other hand, may require more drives. For small mITX or mATX cases, this doesn't present much of an issue, as limited space availability in smaller cases prohibits more than a few drives.
Some motherboards include additional SATA ports, but use drivers that may not be supported by Linux. Therefore, for best Linux compatibility, you should select a motherboard with two SATA ports and no extra frills. Otherwise, you may need Windows 8. Windows 7 users reportedly experienced problems on certain AM1 motherboards.
In a nutshell, two types of operating systems can be installed, out-of-the-box, with little trouble:Linux, on the latest kernel (what's happening with Ubuntu 14.04 Ubuntu users - here's how to upgrade to 14.04, "Trusty Tahr" Ubuntu Users:How to upgrade to 14.04, "Trusty Tahr" with Ubuntu? How to get the latest version. Read More?) And Windows 8:Older versions of Windows require additional drivers to install properly; many board manufacturers do not support AM1. I'd recommend Linux builds over others, though support for AMD's Linux APU driver tends to lag behind Windows 8 builds. Expect higher power and heat consumption as a result. To some extent, users may notice some issues with saving images to frames when trying to stream HD video if using Linux and open source drivers. Fortunately, AMD makes its proprietary drivers available for download (see below).
Building a PC based on the AM1 platform requires a basic understanding of computer assembly. We have written about building your own PC. This section covers the quirks of building on the AM1 platform and the individual components you'll need.
As of May 2014, there are six AM1 APUs. What is an APU, you ask? APUs combine a graphics processor (GPU) with a central processing unit (CPU). There is synergy in this pairing:the APUs require less power than the independent "discrete" GPUs. They also require less space in the box. Unlike discrete GPUs, which include solder-in memory, APUs designate a variable portion of system memory, or RAM, for the APU. Users can configure their APUs to use between 512 MB of RAM to 2 GB. APUs can produce better performance in many games with faster RAM.
RAM speed and dual channel :Unfortunately, AM1 technology does not support dual channel memory. This limits bandwidth, but generally doesn't cause a big performance hit. AM1 technology currently also maxes out at speeds of 1600MHz DDR3. Taking these factors into account, you can create a solid performing AM1 system with a single 4 GB memory stick (thanks to MUO user Howard for the fix).

APUs plugged in Note:AM1 APUs also come “plugged in”, which means you can swap out the APU for another when updates are released. Right now, the Athlon 5350 sits at the top of the APU hierarchy, but over time AMD will likely cycle between AM1+, followed by AM2. Given AMD's previous history, AM1+ APUs will work on AM1 sockets. They will not work on AM2 sockets, so users should be given an upgrade option in 2015. All APUs use 25 watts.

AM1 motherboards come in two form factors:mini-ITX or micro-ATX. The smaller of the two, the mini-ITX (mITX), differs in having only a single PCIe slot, while the mirco-ATX (mATX) boards offer two:one slow, the other fast. To my knowledge, there are about a dozen AM1 boards out there, ranging in price from $30 to about $60. The boards differ from each other by adding features, such as parallel ports, mini-PCIe ports, additional SATA ports, and more. . However, users will experience driver compatibility issues when trying to install Linux on boards with additional features.
Here are some additional dashboards, along with additional capabilities:
Regarding mATX cards, I think the PCIe 2.0 x16 slot offers little, as using a discrete graphics card turns off the integrated graphics. Unless there's a special reason, most builds get better value building using mITX, despite the slightly higher cost of the board. In general, mITX cards fit into smaller cases and require less cable length to make connections.

Before buying the case, please make sure its height can fit the internal 65mm fan. Two cases, which also offer integrated picoPSUs, are the Realan E-i5 and the Realan E-i7. The E-i5 also includes space for two 2.5" drives, while the E-i7 can fit a slim DVD drive. I recommend the 60-watt power supply option, if you're using a solid-state drive. For those with mechanical drives, you may need to upgrade the power supply.Hard drives can use around 25 watts of power at startup, depending on their design.
mITX cases:

mATX cases:

If you don't want to use an integrated power supply, you can purchase one that matches the dimensions of your case. Case manufacturers will indicate the form factor or physical dimensions required by the case. Small form factor cases will use picoPSU, TFX, SFX, or “microatx” power supplies (there isn't really a form factor known as microATX, for power supplies). I should note that TFX and SFX power supplies generally use smaller fans, which spin at faster speeds, causing additional noise. The best unit, in terms of price, remains the picoPSU. Remember the following rules for picoPSUs:They use limited and variable connector types. If a picoPSU does not have the necessary connectors, you will need to purchase a splitter or adapter.
Air mice :I highly recommend getting a media center remote, my favorite:an Air Mouse. Allows you to control your mouse using accelerometers. The movement of the hand holding the remote control also moves the on-screen cursor. Also, you may want to consider a USB or PCIe wireless card. Note however that low profile cases will require low profile PCIe cards.

Infrared remote control :IR remote controls use the infrared spectrum to send commands to your TV. They require an infrared receiver, which can be built into a compatible case or run from a USB stick. IR remotes sometimes offer “universal” compatibility, meaning they can control and a TV. your HTPC. They also don't suffer from the same bandwidth limitations as WiFi-operated remotes. On the downside, they don't feel as good as an Air Mouse.
Dual Band Wi-Fi Adapter Note:If your machine primarily streams video content, check to see if your wireless router offers dual-band support. What is a dual band wireless router? How can dual-band routers solve your wireless problems? How can dual-band routers solve your wireless problems? Read more ? In short, it helps stream content at faster speeds, with much less interference.
First, make sure you've read how to build a computer.
I'm not going to go into the minutiae of PC building. The build process for the AM1 platform does not differ in any important respect from the others. Aside from an AMD CPU brace outlet, putting together an AM1 PC doesn't require any special knowledge. I will briefly explain the main game..
Socket AM1 (which is a rebranded socket FS1b) has more in common with Intel's LGA1150 socket than it does with AMD's. Uses two spring pins. Essentially, you hook the heat sink fan combination onto two plastic guide posts. Then place the heat sink/fan combination over the CPU socket, aligning the guide posts with the holes on the motherboard.
The spring loaded plastic guide posts require a little force to insert into the holes on the heat sink. Make sure you have aligned the guide post handles with the heat sink as they will not fit through the holes in the motherboard. Then push the guide posts through the holes in the motherboard, surrounding the APU socket. Once they have been pushed all the way in, insert the longer pins through the center of the guide posts, which will lock the heat sink in place. There are two of these, so make sure you do one at a time.
You won't need to do much in BIOS/UEFI (referred to as UEFI). Simply load the optimized default, set up a RAM profile, and then designate the amount of RAM you want to supplement your APU with. Then save and exit. You may need to configure your CMS settings (for compatibility reasons), to "Other OS" rather than "Windows 8", if you're doing a Linux build.
I put together three sample builds for those who want to build one of the three stereotypical models:An ultra-low-cost Linux streaming HTPC, a “deluxe” Linux HTPC, and an eco-friendly Windows 8 streaming HTPC, desktop, and lightweight Steam Box.
This particular model takes advantage of the low build costs of the AM1 platform and the dual-core Sempron 2650 APU. For just a few dollars more, however, builders can trade in the quad-core Sempron 3850, with a higher-rated integrated GPU (which I suggest you do). While not as power efficient as its siblings, due to its active cooling power supply, it still offers very low power consumption.

Aunque me refiero a este ejemplo como “de lujo” modelo, en verdad, es decididamente una construcción de bajo presupuesto. También incluí un Air Mouse, que funciona muy bien como ratones / teclados del centro de medios, un adaptador inalámbrico de banda dual USB y una unidad de DVD delgada para usar con la caja Realan E-i7 HTPC, un poco más grande, que incluye una ranura para DVD delgada.
Mientras que el costo total ronda los $ 400, se obtiene calidad estética, eficiencia de vataje y portabilidad. Específicamente, dejé fuera la compatibilidad con Blu-Ray, ya que agrega una cantidad ridícula de gastos generales. Pero debería hacer prácticamente todo lo que se requiere de un centro multimedia, incluida la reproducción de DVD, la emulación de juegos y los juegos ligeros de Steam o Desura..

Esta construcción particular va para el vataje más bajo posible. Utiliza una unidad de estado sólido (¿qué es una SSD? ¿Cómo funcionan las unidades de estado sólido? ¿Cómo funcionan las unidades de estado sólido? En este artículo, aprenderá exactamente qué son las unidades SSD, cómo funcionan y funcionan realmente las unidades SSD, por qué son las unidades SSD tan útil, y el único inconveniente importante para los SSD. Lea más) y Windows 8, ya que los controladores de Windows 8 incurren en menos drenaje que los controladores de Linux. La placa de ASUS permite la baja tensión - conocida como “Desplazamiento de tensión” en UEFI / BIOS de la junta de ASUS. También utiliza una fuente de alimentación eficiente al 96 por ciento. Se debe utilizar en algún lugar entre 15 y 25 vatios..
Teniendo en cuenta que esta es una generación de potencia inferior, podría Considere el uso de RAM de bajo voltaje. Sin embargo, la RAM de bajo voltaje no ahorra mucho en vatios totales. Y podría potencialmente causar un problema combinado con una placa base AM1, que, según se informa, tiene una delicada compatibilidad con la memoria RAM..

En mi compilación, la plataforma AM1 ofrece la combinación correcta de compatibilidad con Linux, eficiencia energética y asequibilidad. Con Ubuntu 14.04 LTS, también puede crear un excelente HTPC por menos de $ 200. No recomendaría gastar más de $ 300 (o $ 400 si busca una licencia de Windows), pero para cualquiera que desee un centro multimedia de Ubuntu o un escritorio orientado a la productividad, considere la posibilidad de construir con la plataforma AM1..